In India, every employer is required to follow the mandatory system of Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on salary. This system entails deducting tax from the source of income, namely the employee’s salary, and then depositing it with the Income Tax Department on the employee’s behalf. The TDS on salary is collected throughout the year and serves as an advance tax payment towards the employee’s annual tax liability.
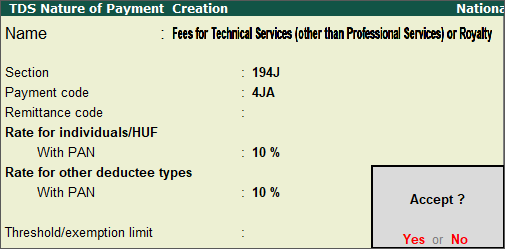
TDS on salary holds significant importance in India’s taxation system, and it applies to all individuals earning a salary. However, comprehending the complex rules and regulations surrounding TDS on salary can be a challenging task for many individuals. In this article, we will cover the fundamentals of TDS on salary, including its calculation, rules, and regulations, to provide a better understanding of this concept.
Understanding the concept of TDS
People can generate income from multiple origins, and they are liable to pay direct taxes, which are determined by the income tax bracket in which their taxable income falls. In India, the taxation system considers Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) to be a crucial component of taxation that affects the after-tax income of taxpayers. Also read section 192 of Income Tax Act, 1961
The Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is a method of direct taxation that was implemented to collect taxes from the source of income or at the time of income distribution. In this mechanism, when a person (deductor) is obligated to pay another person (deductee), they will deduct the tax amount at the source and transfer the remaining balance to the deductee.
The deducted TDS amount will then be submitted to the Central Government. The deductee can check the TDS amount deducted by reviewing Form 26AS or the TDS Certificate provided by the deductor.
TDS serves as a way to prevent tax evasion, and it also removes the burden of paying a lump sum of annual taxes at the end of the financial year for the taxpayer.
Let’s consider an example to gain a better understanding of the meaning of TDS.
Suppose a company, ABC Ltd, is making a payment of Rs. 20,000/- to Mr. X as professional fees, and the specified tax rate is 10%. In this case, ABC Ltd will deduct a tax of Rs. 2,000/- from the payment and transfer the remaining net amount of Rs. 18,000/- (Rs. 20,000/- minus Rs. 2,000/-) to Mr. X. The deducted amount of Rs. 2,000/- will be deposited directly by ABC Ltd to the government’s credit.
Calculating TDS on Salary
The computation of TDS on salary is performed by subtracting the exemption amount from the total annual income of the salaried employee. The exemption limit is established by the Income Tax Department. While calculating the TDS on salary, the employer is required to obtain proof and a declaration from the employee before approving the exemption amount.
The following allowances are eligible for tax exemption:
- House Rent Allowance If an employee is paying rent for accommodation, he/she can claim House Rent Allowance (HRA) from the employer.
- Standard Deduction In place of conveyance and medical allowances, the government has provided a blanket deduction of Rs. 50,000/- known as Standard Deduction.
- Children’s Education Allowance Children’s Education Allowance permits a deduction of Rs. 100 per month per child for up to two children.
- Leave Travel Allowance Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) is a type of allowance offered by the employer to employees. LTA can be used by employees to cover travel expenses while on leave and claim reimbursement from the employer. To be eligible for LTA, it should be a component of the employee’s salary. Additionally, as per Section 10 (5) of the Income Tax Act, 1961, LTA received by the employee is not included in the net taxable income of the employee.
The LTA can only be claimed on either the actual travel cost or the component amount in the employee’s salary breakup, whichever is lesser. However, employees can avail of LTA for two journeys in a block of four years.
Liability of the Employer
The employer is responsible for deducting TDS on salary when making payments to the employee. TDS can only be deducted at the time of payment, and only when the employee’s salary is taxable. However, if the salary is equal to or less than Rs. 2, 50,000 TDS on salary will not be deducted.
As per Section 192, there must be an employer-employee relationship for TDS deduction on salary. The following entities are responsible for making TDS on salary deduction: individuals, private or public companies, HUF (Hindu Undivided Family), trusts, partnership firms, and co-operative societies. The employer’s status, such as company, HUF, or trust, is irrelevant for TDS on salary deduction. Additionally, the number of employees employed by the employer has no impact on the TDS calculation.
How to Claim TDS Refund: A Step-by-Step Guide
The TDS refund occurs when the TDS paid is greater than the actual tax liability for the financial year. Taxpayers can claim a refund for excess TDS deducted on various incomes, such as interest income or salary. When filing their income tax return, taxpayers need to calculate their total tax liability and subtract the TDS applied to their income. If the TDS is higher than the tax liability, a refund is due from the government.
Steps to Claim TDS Refund
If the tax deducted from your income does not match your actual tax liability, you can claim a refund by filing an income tax return (ITR). During the ITR filing process, you need to provide your bank details for the refund to be credited directly to your account.
- If your employer deducts more taxes than your actual tax payable, you can apply for a lower or Nil TDS certificate from your jurisdictional Income Tax Officer in Form 13. By submitting the Nil deduction order under Section 197, you can avoid TDS deduction from your salary. To claim a TDS refund, you need to calculate your income and taxes and file an Income Tax Return (ITR). You must provide bank account and IFSC code details while filing the ITR online for the IT department to process the TDS refund.
- If your taxable income is below the basic exemption limit, you can submit a declaration in Form 15G to your bank at the beginning of the financial year to avoid TDS deduction on your fixed deposit interest income. However, if the bank still deducts TDS, you can claim a refund by filing your income tax return (ITR).
- Senior citizens aged 60 years and above are exempted from tax deductions on interest income earned from FDs, subject to the condition that interest from each bank is less than Rs. 50,000 per year. If the interest income exceeds the limit, but the total income is below the basic exemption limit, then senior citizens can submit Form 15H at the beginning of the financial year to avoid TDS deductions. If TDS is still deducted, they can claim a refund by filing their ITR.
Claim TDS Return Online
- The first step to file your TDS online is to register yourself on the Income Tax department’s website: https://incometaxindia.gov.in/Pages/tax-services/online-filing.aspx
- After registration, you can download the relevant ITR form and fill in the required details. Once you have filled the form, upload it and click on submit.
- After submitting, an acknowledgement will be generated for the ITR submitted, which you need to e-verify.
- There are three methods to e-verify: using a digital signature, an Aadhaar-based OTP, or your net banking account.
- In case you are unable to e-verify the ITR, you can complete the verification process by sending a signed physical copy of the ITR to the IT department
Checking the Refund Status
There are several ways to check the status of your TDS refund.
- Firstly, you can refer to the acknowledgement and refund processing email sent by the IT Department to your registered email address.
- You can also check the TDS refund status on the Income Tax website using your PAN card number.
- Alternatively, you can contact the CPC Bangalore on their toll-free number – 1800-4250-0025
TDS Certificate
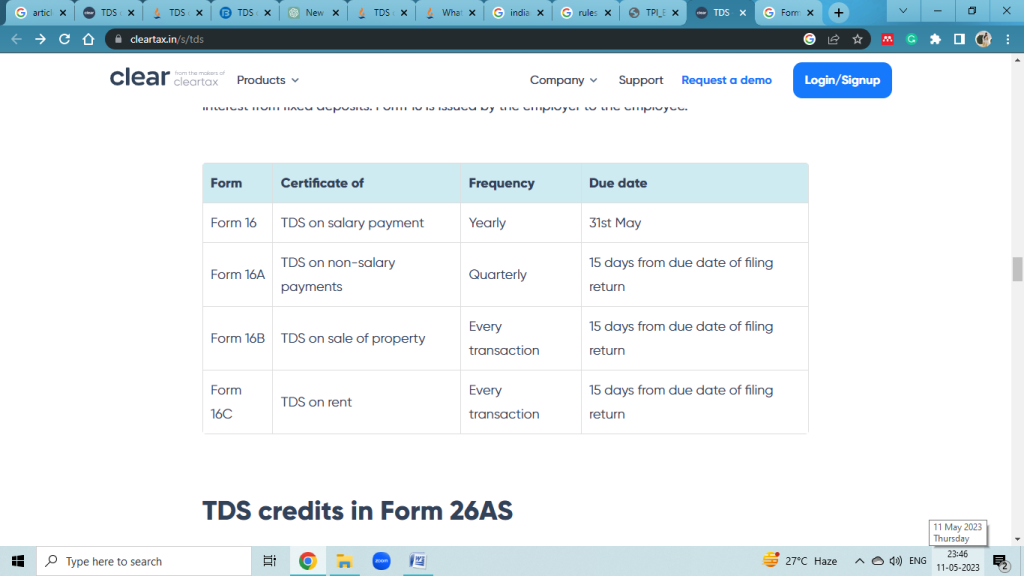
TDS certificates, namely Form 16, Form 16A, Form 16B, and Form 16C, are issued by the individual or organization who deducts TDS from the income paid to the recipient. For example, banks provide Form 16A to depositors after deducting TDS on interest earned from fixed deposits, while Form 16 is issued by employers to employees.
TDS Credits in Form 26AS
TDS deductions are linked to PAN numbers for both the deductor and the deductee, and it is important to mention your PAN correctly wherever TDS may be applicable to your income. The Tax Credit Form 26AS is a consolidated tax statement that lists out the details of TDS deducted on your income by each deductor for all kinds of payments made to you, along with any income tax paid by you directly.
To file TDS returns easily, you can use ClearTDS, online TDS software that requires no download or installation and helps you prepare accurate e-TDS statements and generate TDS certificates.
Conclusion
To sum up, having a clear comprehension of TDS on salary is crucial for all salaried individuals in India. It is necessary to be aware of the TDS rates, exemptions, and deductions to prevent any unwarranted deductions and comply with tax regulations. By following the instructions outlined in this guide, you can proficiently handle your TDS on salary and prevent any difficulties while filing your tax returns. By having a good understanding of TDS, you can ensure that you do not overpay taxes and maintain a favorable financial standing.
FAQs
Q: What is the purpose of TDS in India?
A: TDS or Tax Deducted at Source is a tax collection mechanism in India where a certain percentage of tax is deducted by the payer while making payments to the payee. It ensures that tax is collected by the government in a timely manner and prevents tax evasion.
Q: Can TDS be deducted if PAN is not provided?
A: Yes, TDS can be deducted even if the PAN is not provided. However, in such cases, the TDS rate is usually higher than the standard rate.
Q: Can TDS be avoided?
A: TDS can be avoided if the income earned falls below the taxable limit or if the individual submits Form 15G/15H, which declares that their income is below the taxable limit and hence no TDS needs to be deducted.
Q: Is TDS applicable on rental income?
A: Yes, TDS is applicable on rental income. If the annual rent exceeds Rs. 2.4 lakh, the tenant is required to deduct TDS at the rate of 10% and deposit it with the government.
Q: Can TDS be deducted on payments made to a non-resident?
A: Yes, TDS can be deducted on payments made to a non-resident. The TDS rate varies depending on the nature of the payment and the provisions of the Income Tax Act.
Q: What is the penalty for non-deduction of TDS?
A: If TDS is not deducted, or if it is deducted but not deposited with the government, a penalty can be levied by the Income Tax Department. The penalty can range from 1% to 1.5% per month for the period of delay.
Q: What is the difference between TDS and TCS?
A: TDS or Tax Deducted at Source is a tax collection mechanism where a certain percentage of tax is deducted by the payer while making payments to the payee. TCS or Tax Collected at Source is a similar mechanism, but the tax is collected by the seller at the time of sale. TCS is applicable on certain goods and services specified by the government.
Q: Can TDS be claimed as a deduction while filing income tax returns?
A: Yes, TDS can be claimed as a deduction while filing income tax returns. The TDS amount deducted can be claimed as a credit against the total tax liability of the taxpayer.

