Introduction
In the steadily developing cricket scene, technology has become a key partner, offering a way to improve the exactness of decision production and infuse fairness into the game. The Decision Review System (DRS) is the key to this technological transformation, a device intended to help umpires make additional educated choices using different technological guides.
Since its origin, the DRS has been a subject of extreme scrutiny and discussion, with defenders praising its part in decreasing umpiring mistakes and pundits scrutinizing its viability and effect on the conventional texture of the game. In this article, we dig into the complexities of the DRS, investigating its development, parts, debates, and more extensive ramifications for the sport of cricket. We are talking about Interpreting the Debate: Understanding the Elements of the Decision Review System (DRS).
Here we are discussing about Interpreting the Debate: Understanding the Elements of the Decision Review System (DRS):
Advancement of the DRS

The Decision Review System’s starting points can be traced back to exploratory stages in the mid-2000s, with the International Cricket Council (ICC) authoritatively executing it in Test cricket in 2009. At first met with skepticism and opposition from a few cricketing countries, the DRS continuously acquired acknowledgment and extended its presence to incorporate One-Day Internationals (ODIs) and Twenty20 Internationals (T20Is).
Parts of the DRS
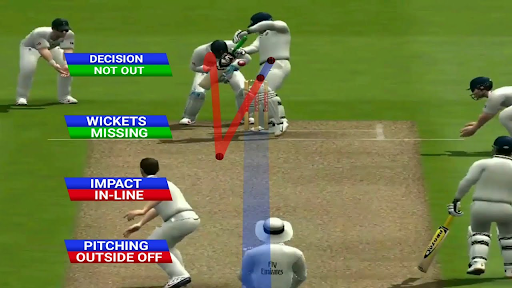
At its center, the DRS contains three essential parts:
Ball Tracking Technology: Using sophisticated ball-tracking systems, such as Hawk-Eye, the DRS visually represents the ball’s trajectory from the second it is delivered by the bowler to its focal point with the batsman or the stumps. This technology empowers umpires to more precisely review decisions connected with LBW (Leg Before Wicket) requests.
UltraEdge: Utilizing audio-visual technology, UltraEdge helps determine whether the ball has connected with the bat or some other piece of the batsman’s equipment before being gotten by defenders or stirring things up around town. This part assumes a vital part in adjudicating got-behind and trapped-in-the-field decisions.
Hot Spot: Hot Spot uses infrared imaging to distinguish heat created by rubbing when the ball connects with the bat or the batsman’s cushions. This intensity signature is then analyzed to ascertain bat-cushion avoidances and weak edges, supporting umpires in settling on additional educated choices.
Debates Encompassing the DRS

Despite its planned motivation behind lessening umpiring mistakes and guaranteeing fairness, the DRS has been entangled in different debates throughout the long term:
Umpiring Discretion: One of the essential reactions evened out against the DRS is its dependence on the on-field umpire’s discretion to start reviews. This discretionary power has prompted instances where groups have been disadvantaged because of the disappointment of umpires to review possibly erroneous decisions.
Technology Restrictions: While the DRS uses advanced technological devices, it isn’t reliable. Specialized errors and impediments in specific circumstances, like inclement climate or unfortunate light, feel somewhat skeptical about the system’s dependability and exactness.
Influence on the Soul of the Game: Conservatives contend that the presentation of technology, especially in decision-production processes, sabotages cricket’s substance as a talent-based contest, judgment, and human blunder. They fight that dependence on machines reduces the inborn show and unconventionality valued in the game for some time.
Lopsided Execution: Variations in the accessibility and use of the DRS across various cricketing countries have additionally powered discussions. A few groups have voiced concerns concerning the apparent unfairness coming about because of the shortfall of consistency in the utilization of technology during matches.
More extensive Ramifications and Future Possibilities
Past the domain of argumentative discussions, the DRS has had extensive ramifications for the sport of cricket:
Upgraded Decision-Production: Notwithstanding its flaws, the DRS has undoubtedly improved the accuracy of decision-making in cricket, limiting glaring mistakes and giving players a response to challenging, quarrelsome decisions.
Development of Strategies: The presentation of the DRS has incited groups to take on essential ways to deal with its use, with skippers and players utilizing strategies to boost their possibilities of fruitful reviews. This strategic perspective adds one more layer of intricacy to the game, expecting groups to adjust their assets wisely.
Technological Headways: The turn of events and refinement of advances related to the DRS keep advancing, with developments pointing toward tending to existing limits and improving the system’s general viability. Future headways might incorporate the joining of man-made reasoning and AI calculations to further increase decision-production processes.
Saving the Integrity of Cricket: While joining technology might inspire anxiety among idealists, guaranteeing the integrity and fairness of cricket stays fundamental. As the game develops, finding harmony among custom and advancement will be critical in keeping up with cricket’s allure and significance in cutting-edge times.
FAQs
What is the Decision Review System (DRS)?
The Decision Review System, generally known as DRS, is a technological device utilized in cricket to help umpires settle on additional precise choices regarding different parts of the play, like LBW (Leg Before Wicket) requests, gets, and dismissals.
How does the DRS work?
The DRS involves a few parts, including ball tracking technology (e.g., Hawk-Eye), UltraEdge, and Hot Spot. These advances give visual and audio help to assist umpires with reviewing combative decisions made throughout play.
What are the essential parts of the DRS?
The primary parts of the DRS include:
Ball Tracking Technology tracks the direction of the ball to decide its probability of raising a ruckus around town in LBW decisions.
UltraEdge: Uses audio-visual technology to identify bat-ball contact, aiding decisions concerning gets and edges.
Hot Spot: This uses infrared imaging to distinguish heat marks brought about by contact, helping with the identification of faint edges and bat-cushion avoidance.
Who can demand a review utilizing the DRS?
By and large, players on the field, regularly on the handling side, can demand a review of an umpire’s decision. Be that as it may, specific circumstances and rules administer when and how reviews can be mentioned, including the number of reviews accessible per inning and the planning of the solicitation.
Might any decision at any point be reviewed utilizing the DRS?
No explicit decisions, such as LBW decisions, get, and dismissals, can be reviewed using the DRS. Nonetheless, not all decisions on the field are reviewable, and there are constraints on the sorts of episodes that can be reviewed.
How precise is the DRS?
While the DRS has further developed decision-production precision in cricket, it isn’t trustworthy. The system’s exactness depends upon different elements, including the nature of the technology utilized, ecological circumstances, and umpires’ judgment in deciphering the proof given by the DRS.
What are a few controversies encompassing the DRS?
The DRS has been entangled in controversies connected with its dependence on umpire attentiveness, technological constraints, its effect on the soul of the game, and aberrations in its execution across various cricketing countries.
How has the DRS affected the sport of cricket?
The DRS has had critical ramifications for cricket, including improved decision-production exactness, development of strategic techniques among groups, technological advances, and progressing discussions concerning the harmony between tradition and innovation.
Are there any continuous turns of events or possibilities for the DRS?
The DRS keeps on advancing inside.
Continuous efforts to improve precision and unwavering quality are combined with computerized reasoning and AI advancements. Future progressions plan to address existing limitations and further upgrade the system’s adequacy in helping umpires and guaranteeing reasonableness in cricket.
Is the DRS acknowledged and carried out in all types of cricket?
While the DRS has acquired wide acknowledgment and use in global cricket, its execution fluctuates across various cricketing countries and configurations. A few homegrown associations and competitions might decide not to embrace the DRS because of strategic or monetary limitations, prompting differences in its accessibility and use.
Conclusion
The Decision Review System is a testament to cricket’s readiness to embrace technological progressions as it looks for fairness and precision. Regardless of its contentions and difficulties, the DRS addresses a critical step in the right direction in the development of the game, offering players and authorities a way to correct mistaken decisions and maintain the integrity of the game. As cricket keeps on exploring the complexities of custom and development, the job of the DRS will stay a subject of continuous scrutiny and discussion, molding the future trajectory of the game for a long time into the future.

