The full form of WAN is a Wide-Area Network. It quickly established itself on a worldwide scale and may be used to link several devices together globally. This form of network makes better communication between devices everywhere in the world possible. Today, the Internet is acknowledged as the most extensive and fastest-growing wide-area network in the world, facilitating global connectivity. Here, we are talking about Full form of WAN.
The full form of Wide Area Network
WAN greatly aids the development of communication in communities, corporations, and organizations. Wide area networks are the most well-known computer or system networks now available internationally since they are a typical type of telecommunication network that may be utilized from any point in the globe.
Introduction
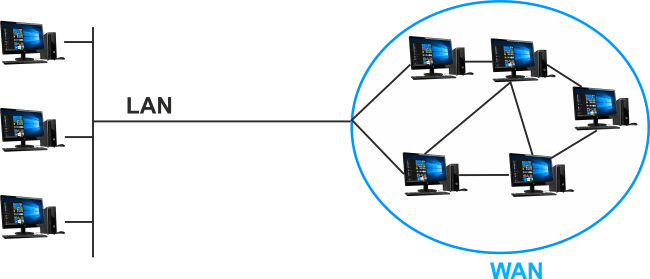
To put it simply, a Wide-Area Network (WAN) is a collection of connections between several devices made through Local Area Networks or other networks that may interact with one another across considerable distances. WANs are networks of networks, and the Internet is the largest WAN in the world.
Service providers assist in the provision of the wide area networks. For instance, companies like JIO, IDEA, AIRTEL, VI, and others are examples of service providers in the context of SIM and cellular networks. Users are often charged a fee in exchange for access to their networks. If a customer is inside the service provider’s network coverage area, they can send or receive messages from any location to any other location.
Wide Area Networks are great because they offer better security than conventional networks and give each connected device a distinct IP address. An IP address is logged and acknowledged as the network’s identity whenever a data transaction occurs. A service provider will normally utilize it to find a particular device.
There are primarily two types of wide-area networks. The first works with a point-to-point connection, whereas the second moves packet data.
The full form of Wide Area Network
This network requires a WAN router, an edge or border router. A WAN router connects the hardware components that allow data packets between wide-area network sites and grant a company access to a carrier network.
History of wide-area networks
The U.S. Air Force created the first Wide Area Network in the late 1950s. Significant academics could interact and share computer resources remotely thanks to the ARPANET, which originated in the US military when it was created. Radio waves, circuit-switched telephone lines, or optical fibers were used to establish communication.
Since then, it has undergone significant development and has shown to be helpful in the global exchange of information between individuals. Thanks to these networks, a buyer and a seller, a teacher and a student, a customer and an employee, etc., may now communicate. A key benefit is the ability of a wide area network to transport data in several digital formats across great distances.
How do WAN protocols work?
The guidelines for communication on any network are set out by wide-area network (WAN) protocols, often known as networking protocols. These are a few instances:
Relay frames
An early technique called frame relay sends data in frames across a private line to a frame relay node. Frame relay allows information to flow from one LAN to another via several switches and routers and operates on layers 1 and 2.
In-between transfer mode
Data is formatted into 53-byte data cells using the early WAN technology known as Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). Time-division multiplexing is a technique used by ATM network devices to divide digital signals into fixed-sized cells, transmit those cells, and then reassemble those cells at their destination.
Packet via SDH/SONET
A communication protocol known as Packet over SONET/SDH (POS) establishes the rules for point-to-point communications utilizing optical fiber.
TCP/IP
End-to-end communication is defined by the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), which outlines the proper methods for packetizing, addressing, transmitting, routing, and receiving data. The most recent iteration of the most widely used technique is IPv6.
Optimizing WAN
Business performance issues are frequently brought on by network latency and capacity issues. With the aid of several techniques, such as network shaping, protocol optimization, reduction, compression, and local caching, Wide Area Network makes use of optimum optimization practices. These methods help the network function better and enhance packet delivery. In the end, this aids in lateral traffic control and enables dynamic network capacity expansion or reduction as required.
The full form of Wide Area Network
What a Wide Area Network Looks Like?
- A wider audience: The wide area network has a huge coverage area. A complete country, a large region, or even the entire planet may be covered by WAN.
- Greater Capacity: The wide area network has a far higher capacity than the local area network. As a result, it easily links a big number of users across various places in the world, demonstrating its ability to connect a huge number of devices.
- Wide area networks link and transfer data fast using public carriers like telephone networks, cable systems, satellites, etc., since these resources are widely accessible.
- Resource Sharing: A wide area network enables users to exchange data and information over vast world regions. Computer resources may be conveniently managed through remote devices that exchange data fast.
Wide Area Network Benefits
- A wide area network’s key characteristic is its coverage over a sizable geographic area, which facilitates quick and simple data transfer.
- Due of WAN’s ability to provide distant data access, the data may be stored effectively and efficiently.
- WAN can help cut down on the amount of travel required to cover vast geographic areas.
- One of the finest features of a wide area network is its ability to swiftly connect individuals and organizations worldwide, facilitating data exchange and enabling worldwide business communication.
Wide-area network advantages
- WAN aids a centralized data workflow, which implies that all workstations may share data via the primary server.
- Because WAN spans a vast geographic region, data transport is rapid and reasonably priced.
- It reduces travel expenses and shares the effort.
- A user or workstation may connect to the rest of the world through WAN, allowing them to exchange data and do business internationally.
The full form of Wide Area Network
Wide-area network disadvantages
- A lot of traffic is being translated between data transfers in a vast area network.
- The vast area network offers less security than the LAN (local area network) or MAN (metropolitan area network).
- A wide area network has a little more significant startup cost than others.
- Another disadvantage of a wide area network is that when enormous amounts of data are being transferred simultaneously over several links, noise and mistakes are present in significant quantities.
- Because a WAN involves several connections and long-distance transactions inside the network, data transmission speeds are slower in a WAN than in a local area network.
Different WAN Technology Types
- Switching packets: Data is transferred in many portions using a form of data transport known as packet switching, often known as TCP/IP. The two most widely used protocols for data communication are TCP (transmission control protocol) and IP (internet protocol). Today’s Internet and particular computer/device networks use the TCP/IP family of core communication protocols to connect network components.
- Router: A router is a piece of hardware used to connect various devices to a network. It functions as a network device with input and output.
The full form of Wide Area Network

