The Central Processing Unit, or CPU, is the brain of a computer system. It is responsible for executing instructions of a computer program by performing arithmetic, logical, and input/output (I/O) operations. This article will discuss What is the full form of CPU, its components, and its functions.CPU stands for “Central Processing Unit,” which serves as the primary brain of a computer, responsible for executing instructions, performing calculations, and managing data processing tasks. In this article, we will delve into the full form of CPU and explore its significance in computing.
Understanding the Central Processing Unit (CPU):
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is often called a computer’s ” brain, ” as it carries out most of the processing tasks necessary for the system to function. It interprets instructions from software programs, performs arithmetic and logical operations, and coordinates the activities of other hardware components to execute tasks efficiently. The term “CPU” is a fundamental component in the world of computing, playing a pivotal role in the functionality of computers and electronic devices.
What is the full form of CPU?
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit. The CPU is a microprocessor that acts as the primary processing unit of a computer system. It controls all the other parts of the computer system and carries out all the instructions in a computer program.
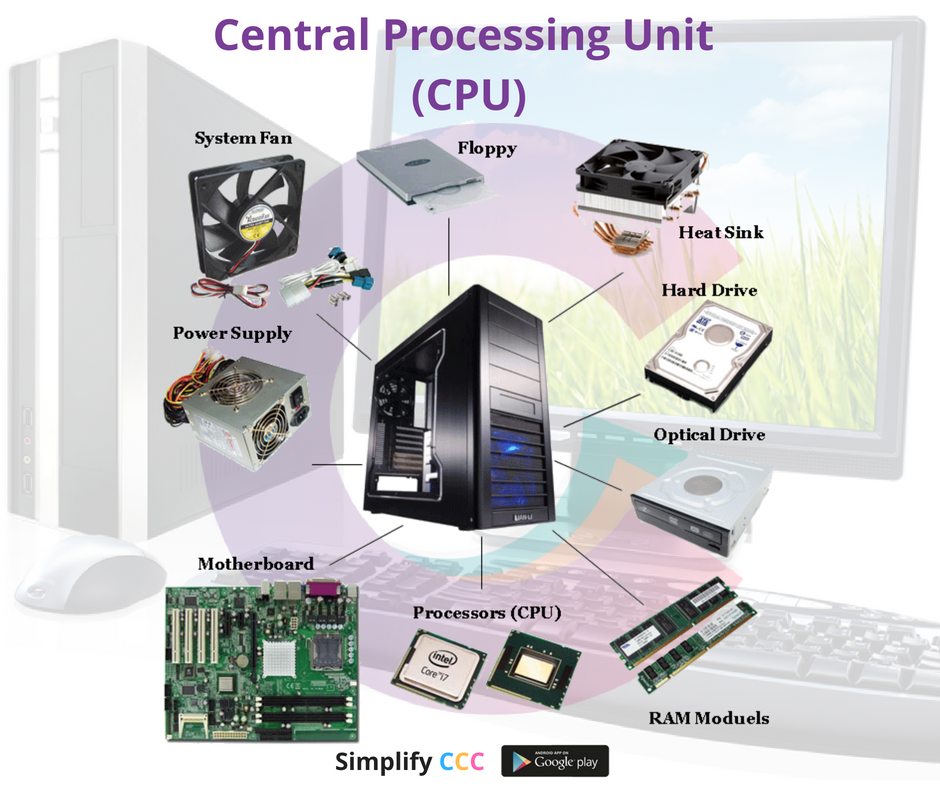
Components of a CPU
A CPU consists of three main components: the control unit (CU), the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and the memory unit (MU). The control unit fetches instructions from memory and decodes them so that the CPU can execute them. The arithmetic logic unit performs arithmetic and logical operations. The memory unit stores data and instructions.
- Control Unit (CU): The Control Unit is responsible for coordinating and controlling the operations of the CPU. It fetches instructions from memory, decodes them, and executes them by issuing commands to other parts of the computer system.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): The Arithmetic Logic Unit is the component of the CPU that performs arithmetic operations (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) and logical operations (such as AND, OR, and NOT) on data.
- Registers: Registers are small, high-speed storage locations within the CPU that temporarily store data during processing. They hold instructions, data, and addresses currently being processed by the CPU.
- Cache Memory: Cache memory is a type of high-speed memory located within the CPU that stores frequently accessed data and instructions, allowing the CPU to access them quickly and efficiently.
Functions of a CPU
The CPU is responsible for executing the instructions of a computer program. It performs various functions such as fetching, decoding, executing, and storing instructions. It also performs arithmetic and logical operations and communicates with other devices in the computer system.
- Fetch
The CPU fetches instructions from memory. The instruction specifies the operation that needs to be performed, and the CPU interprets it.
- Decode
The CPU decodes the instruction, breaking it down into smaller parts that the CPU can understand.
- Execute
The CPU performs the operation specified by the instruction. This operation could be arithmetic, logical, or involve I/O operations.
- Store
The CPU stores the result of the operation in memory or sends it to other devices for further processing.
FAQs about CPU
What is a CPU?
A CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is a hardware component of a computer system responsible for executing instructions, performing calculations, and coordinating the activities of other hardware components. It is often described as the brain of the computer, as it interprets and executes program instructions and manipulates data according to those instructions.
What are the main functions of a CPU?
The primary functions of a CPU include fetching program instructions from memory, decoding these instructions into commands the CPU can understand, executing the commands, and then storing the results back into memory. Additionally, the CPU manages data processing tasks, performs arithmetic and logical operations, and coordinates communication between different hardware components.
What are the components of a CPU?
A CPU typically consists of three main components:
- Control Unit (CU): Responsible for fetching instructions from memory, decoding them, and coordinating the execution of these instructions.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Performs arithmetic and logical operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and comparisons.
- Registers: Small, high-speed storage units used to store data temporarily during processing. Registers include the instruction register (IR), program counter (PC), and various general-purpose registers.
How does a CPU execute instructions?
The CPU executes instructions in a series of steps known as the instruction cycle, which typically includes the following stages:
- Fetch: The CPU fetches the next instruction from memory using the program counter (PC).
- Decode: The fetched instruction is decoded by the control unit to determine the operation to be performed.
- Execute: The ALU executes the instruction, performing the specified operation on the data.
- Store: The result of the operation is stored back into memory or a register, depending on the instruction.
What factors determine the performance of a CPU?
Several factors influence the performance of a CPU, including clock speed (measured in gigahertz), number of cores, cache size, architecture, and efficiency of instruction execution. Higher clock speeds, more cores, larger cache sizes, and advanced architectures typically result in better CPU performance and faster processing speeds.
What are some common CPU manufacturers?
Some of the leading CPU manufacturers include Intel Corporation, known for its Intel Core and Intel Xeon processors, and Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), known for its Ryzen and EPYC processors. These companies design and produce CPUs for a wide range of computing devices, from desktops and laptops to servers and supercomputers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the CPU is the primary processing unit of a computer system. It is responsible for executing computer program instructions by performing arithmetic, logical, and I/O operations. The CPU consists of three main components: the control unit, the arithmetic logic unit, and the memory unit. The CPU performs various functions, such as fetching, decoding, executing, and storing instructions. Understanding the full form of the CPU and its functions is crucial in comprehending how a computer system works.

